Resolving VPN Tunnel Instability Through Real-Time Performance Analysis
 Reliable VPN tunnels are essential for maintaining secure communication between branch offices, data centers, cloud environments, and remote users. When a VPN tunnel fails or performance degrades, the impact is often immediate, affecting application access, remote work, and business operations that rely on consistent connectivity across geographically distributed environments.
Reliable VPN tunnels are essential for maintaining secure communication between branch offices, data centers, cloud environments, and remote users. When a VPN tunnel fails or performance degrades, the impact is often immediate, affecting application access, remote work, and business operations that rely on consistent connectivity across geographically distributed environments.
As networks expand, troubleshooting VPN tunnel issues becomes increasingly complex. Multiple firewalls, WAN links, ISPs, routing domains, and security policies introduce dependencies that are difficult to track without centralized visibility. In many organizations, VPN problems are only identified after users report disruptions, making root-cause analysis more time-consuming and operationally disruptive.
Key Topics Covered
- Why VPN tunnels commonly experience issues
- VPN tunnel parameters that should be monitored
- Troubleshooting VPN issues using performance visibility
- VPN tunnel flapping during peak hours
- Managing VPN tunnels across multiple firewall vendors
- VPN Tunnel Remains Up but Applications are Slow
- IPsec Negotiation Failures After Configuration Changes
- Asymmetric Traffic and Routing Anomalies
- Gradual Bandwidth Saturation Over Time
- Bringing Performance and Security Checks Together
- Practical Monitoring Habits That Prevent Major Incidents
- Summary
Related Articles
- Boost Firewall Security with Automation: Compliance, Vulnerability, Validation & Real-Time Control
- Enhance Firewall Performance, Security Posture, and Compliance with Unified Network Monitoring
- Cisco ASA - Firepower Articles
- Configuring Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco Routers
- Configuring Point-to-Point GRE VPN Tunnels - Unprotected GRE & Protected GRE over IPSec Tunnels
- Configuring IPSec VPN between Palo Alto Firewall & Meraki MX Security Appliance
Explore a Comprehensive Enterprise-Grade Hybrid Infrastructure Monitoring Platform
Why VPN Tunnels Commonly Experience Issues
VPN tunnels, particularly IPsec-based site-to-site tunnels, rely on multiple tightly coupled components working in precise alignment. Any inconsistency across encryption settings, authentication methods, routing policies, or WAN conditions can result in tunnel instability, partial connectivity, or complete failure.
Configuration mismatches remain one of the most frequent causes of VPN issues. Encryption algorithms, hashing methods, Diffie-Hellman groups, and security association lifetimes (SA) must match exactly on both tunnel endpoints. These mismatches are often introduced unintentionally during firewall policy updates, platform migrations, or firmware upgrades.
WAN-related conditions such as packet loss, latency, jitter, or ISP link congestion also contribute significantly to VPN instability. These issues tend to appear during peak usage periods and may resolve without intervention, making them difficult to diagnose without continuous monitoring and historical trend analysis.
Routing changes further complicate VPN reliability. Incorrect static routes, dynamic routing advertisements, or policy-based routing rules can redirect traffic away from the tunnel. In such cases, the VPN may appear operational while applications silently fail to communicate.
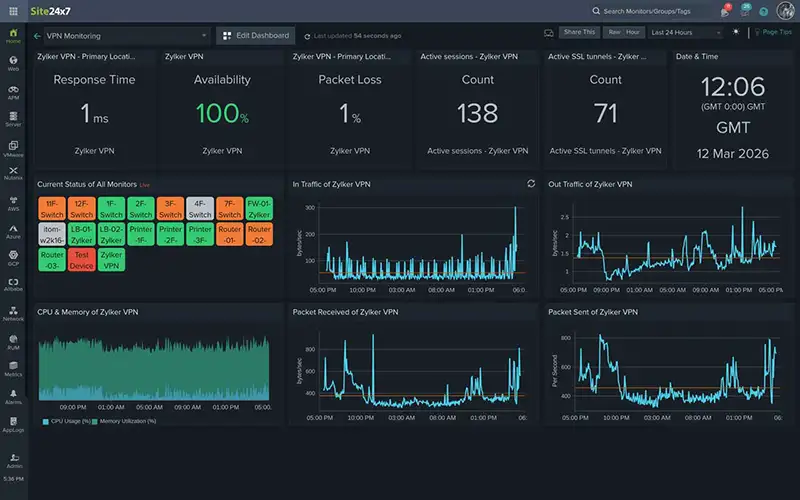
VPN Tunnel Parameters That Should Be Monitored
Effective VPN troubleshooting requires visibility into both security negotiation details and real traffic behavior. Monitoring the correct tunnel parameters allows administrators to identify early warning signs before users are impacted and reduces reliance on reactive log-based troubleshooting.
| Parameter | What It Indicates | Why It Matters |
| Peer identity: | Remote VPN endpoint | Identifies the affected site or branch |
| Encryption algorithm: | Cipher used during negotiation | Detects mismatches preventing tunnel establishment |
| Hashing method: | Integrity verification mechanism | Ensures security association consistency |
| Tunnel operational state: | Up, down, or negotiating | Confirms tunnel usability |
| Inbound traffic: | Traffic received from the peer | Validates application data delivery |
| Outbound traffic: | Traffic sent to the peer | Highlights congestion or routing issues |
Table 1: List of VPN parameters and common associated issues
When these parameters are reviewed together, patterns often emerge that are not visible when examining logs or tunnel state alone. For example, a tunnel may remain established while outbound traffic increases and inbound traffic remains minimal, indicating asymmetric routing or upstream filtering.
Troubleshooting VPN Issues Using Performance Visibility
Performance visibility plays a critical role in diagnosing VPN issues that are not immediately apparent from tunnel status. A tunnel reporting an operational state does not guarantee acceptable application performance or user experience.
Latency, packet loss, and throughput trends often reveal underlying problems long before a tunnel fails outright. By continuously tracking these metrics, administrators can establish baselines and quickly identify abnormal behavior.
Historical performance data is particularly valuable during incident analysis. Rather than relying solely on logs generated after a failure, teams can review performance trends leading up to the event, helping to distinguish between configuration errors and WAN-related constraints.
VPN Tunnel Flapping During Peak Hours
VPN tunnel flapping, characterized by frequent transitions between up and down states, is commonly associated with bandwidth exhaustion or unstable WAN conditions.
By correlating tunnel state changes with throughput metrics, administrators can confirm whether instability aligns with traffic spikes. In many cases, the tunnel configuration itself is correct, but insufficient bandwidth or lack of traffic prioritization causes repeated renegotiation.
Historical analysis allows teams to verify whether similar patterns have occurred previously and whether remediation actions such as traffic shaping, QoS policies, or circuit upgrades have improved stability.
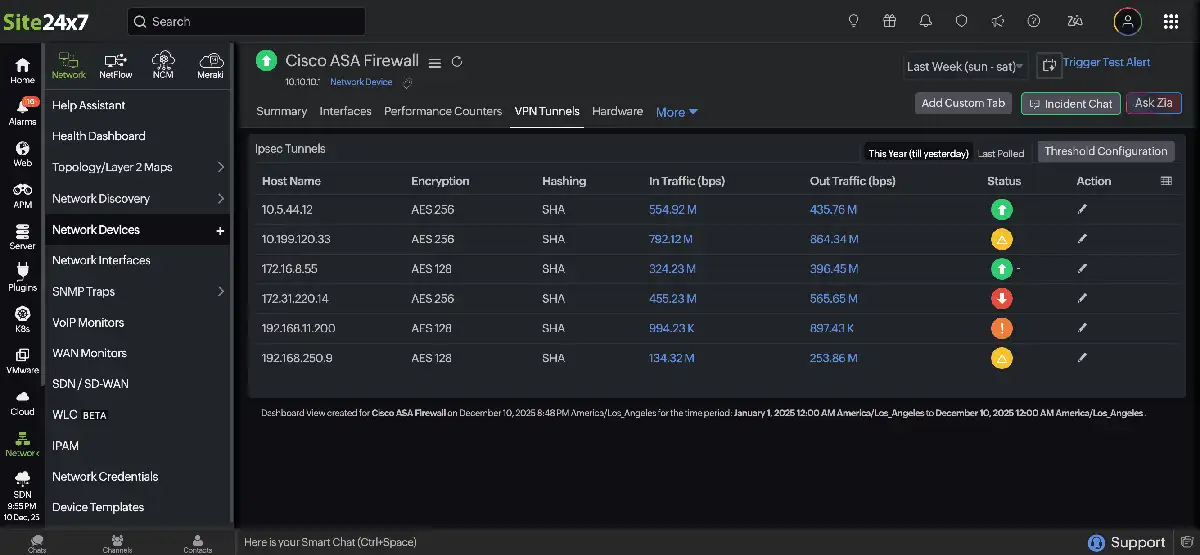
Managing VPN Tunnels Across Multiple Firewall Vendors
Many organizations operate VPN tunnels across different firewall vendors due to mergers, acquisitions, or evolving infrastructure requirements. Each platform introduces its own management interface, terminology, and logging mechanisms.
During incidents, switching between multiple consoles increases troubleshooting time and the likelihood of missing key indicators. A centralized monitoring approach simplifies this process by presenting tunnel state, security parameters, and performance metrics in a consistent format regardless of vendor.
This unified visibility supports faster fault isolation and enables long-term analysis of tunnel reliability and capacity trends across the network.
VPN Tunnel Remains Up but Applications Are Slow
A VPN tunnel may report an operational “up” state while users experience slow file transfers, delayed application responses, or unstable remote sessions. In these cases, the issue often lies not in tunnel establishment but in performance degradation within the encrypted path.
By monitoring latency, packet loss, and retransmission rates alongside tunnel state, administrators can determine whether the encrypted link is introducing excessive delay or whether the underlying WAN circuit is congested. Comparing current metrics against historical baselines helps identify abnormal performance patterns that are not immediately visible from device logs.
Continuous visibility into tunnel throughput and round-trip times enables teams to isolate whether the bottleneck exists within the local network, across the WAN link, or at the remote endpoint.
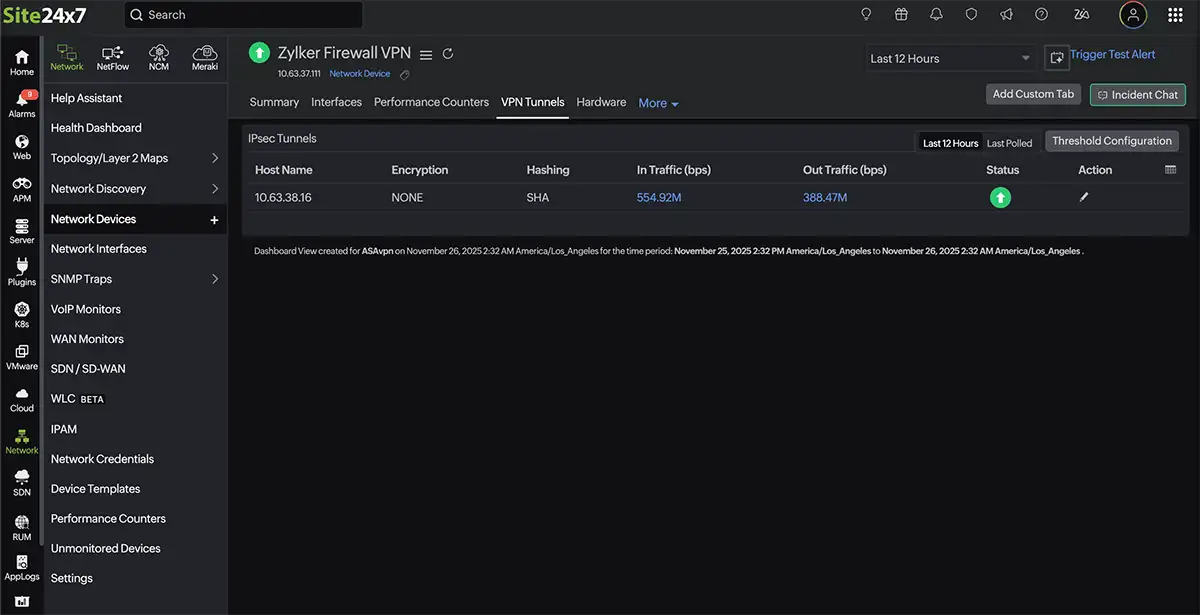
IPsec Negotiation Failures After Configuration Changes
VPN tunnels frequently fail to establish following firewall upgrades, security policy changes, or certificate renewals. Even minor differences in encryption algorithms, hashing methods, or security association lifetimes can prevent successful IKE negotiation.
Monitoring security parameters such as encryption type, hashing consistency, and tunnel negotiation status allows administrators to quickly identify mismatches between peers. Instead of manually reviewing configuration files across devices, centralized visibility into negotiation attributes helps pinpoint discrepancies immediately.
Tracking historical configuration state also makes it easier to correlate tunnel failures with recent changes, reducing the time required to restore connectivity.
Asymmetric Traffic and Routing Anomalies
In some cases, outbound traffic flows through the VPN tunnel correctly while inbound responses fail to return along the same path. This asymmetric routing behavior can cause applications to hang or partially load despite the tunnel remaining active.
By analyzing inbound and outbound traffic levels simultaneously, administrators can detect imbalance patterns that indicate routing inconsistencies or upstream filtering. Performance monitoring platforms that visualize both directions of traffic help uncover these anomalies quickly.
Correlating routing updates or WAN failover events with changes in traffic symmetry further supports root cause analysis and reduces reliance on speculative troubleshooting.
Gradual Bandwidth Saturation Over Time
Not all VPN issues occur suddenly. Gradual increases in encrypted traffic volume can slowly push WAN circuits toward capacity limits, leading to intermittent packet loss and performance instability.
Continuous monitoring of tunnel throughput trends makes it possible to identify sustained growth patterns rather than isolated spikes. Historical performance data provides insight into whether usage is steadily increasing due to business expansion, new cloud services, or increased remote work adoption.
By reviewing long-term bandwidth trends, teams can plan circuit upgrades or implement traffic prioritization before users experience noticeable disruption.
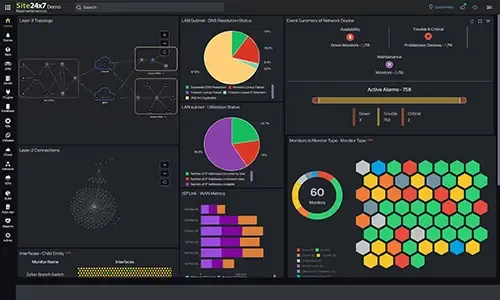
Bringing Performance and Security Checks Together
Effective VPN troubleshooting requires visibility into both security negotiation parameters and real-time performance metrics. Monitoring tunnel state alone is not sufficient; administrators must correlate encryption settings, routing behavior, latency, packet loss, and throughput to accurately identify root causes.
Modern monitoring platforms consolidate tunnel statistics from supported firewalls and combine them with broader network performance monitoring data. Viewing IKE status, encryption parameters, inbound and outbound traffic, and WAN latency in a single dashboard allows teams to determine whether instability is caused by configuration mismatches or transport-layer congestion.
Threshold-based alerting further improves response time. Instead of reacting after a tunnel drops, administrators can define acceptable baselines for availability and performance metrics. When deviations occur, contextual alerts highlight the affected peer and metric, reducing troubleshooting time.
In multi-vendor environments, integrating VPN data with firewall monitoring insights provides additional clarity by correlating tunnel behavior with device health and interface statistics. Bringing security checks and performance visibility together enables faster, data-driven remediation rather than relying on manual log inspection or assumption.
Practical Monitoring Habits That Prevent Major Incidents
Proactive monitoring practices reduce the likelihood of unexpected VPN outages and improve overall tunnel stability. Small configuration or performance anomalies, when detected early, can often be resolved before they affect users.
- Verify tunnel parameters after any firewall policy update, firmware upgrade, or certificate renewal to prevent negotiation mismatches.
- Monitor inbound and outbound traffic symmetry to quickly detect routing inconsistencies or asymmetric flow issues.
- Investigate recurring up/down cycles or renegotiation events even when no complaints have been reported, as these often indicate underlying instability.
- Compare current throughput levels against historical baselines to identify gradual bandwidth saturation and support capacity planning.
- Consolidate tunnel visibility within a centralized monitoring platform—such as network monitoring dashboards—to reduce response time and maintain consistent oversight across all VPN peers.
Summary
Effective VPN tunnel troubleshooting requires more than confirming a tunnel is up. Diagnosing IPsec VPN issues, tunnel flapping, routing anomalies, or bandwidth saturation depends on continuous visibility into encryption parameters, tunnel uptime, latency, packet loss, and throughput trends. When these metrics are consolidated instead of scattered across multiple firewalls and logs, root cause analysis becomes faster and more precise.
By correlating tunnel state with real-time network performance visibility, Site24x7 helps IT teams identify whether instability stems from negotiation failures, asymmetric traffic, or WAN congestion. Proactive alerting and historical trend analysis support proactive VPN monitoring, reduce mean time to resolution, and improve capacity planning — ensuring site-to-site VPN connectivity remains stable, secure, and aligned with business continuity requirements.
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!