All-in-one protection for Microsoft 365
All-in-one protection for Microsoft 365


OpManager: Network & DC Monitoring
Monitor & Manage Network, Datacenters, endpoints & more.
Latest Articles
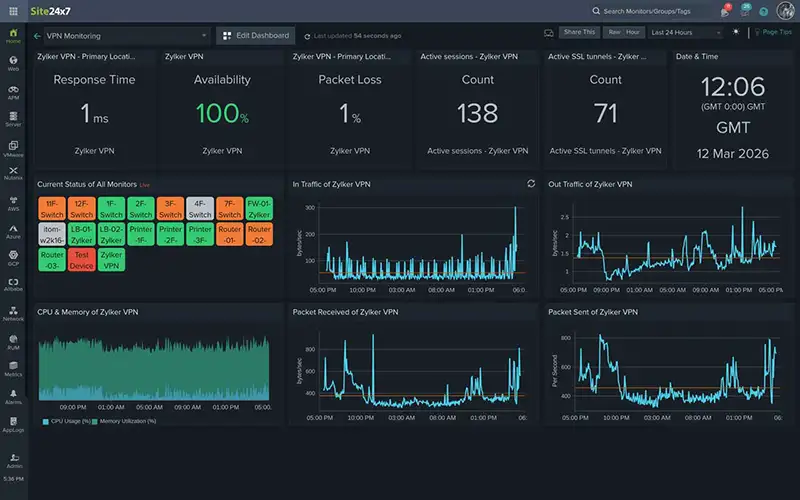
Resolving VPN Tunnel Instability Through Real-Time Performance Analysis
 Reliable VPN tunnels are essential for maintaining secure communication between branch offices, data centers, cloud environments, and remote users. When a VPN tunnel fails or performance degrades, the impact is often immediate, affecting application access, remote work, and business operations that rely on consistent connectivity across geographically distributed environments.
Reliable VPN tunnels are essential for maintaining secure communication between branch offices, data centers, cloud environments, and remote users. When a VPN tunnel fails or performance degrades, the impact is often immediate, affecting application access, remote work, and business operations that rely on consistent connectivity across geographically distributed environments.
As networks expand, troubleshooting VPN tunnel issues becomes increasingly complex. Multiple firewalls, WAN links, ISPs, routing domains, and security policies introduce dependencies that are difficult to track without centralized visibility. In many organizations, VPN problems are only identified after users report disruptions, making root-cause analysis more time-consuming and operationally disruptive.
Key Topics
- Why VPN tunnels commonly experience issues
- VPN tunnel parameters that should be monitored
- Troubleshooting VPN issues using performance visibility
- VPN tunnel flapping during peak hours
- Managing VPN tunnels across multiple firewall vendors
- VPN Tunnel Remains Up but Applications are Slow
- IPsec Negotiation Failures After Configuration Changes
- Asymmetric Traffic and Routing Anomalies
- Gradual Bandwidth Saturation Over Time
- Bringing Performance and Security Checks Together
- Practical Monitoring Habits That Prevent Major Incidents
- Summary
Related Articles
- Boost Firewall Security with Automation: Compliance, Vulnerability, Validation & Real-Time Control
- Enhance Firewall Performance, Security Posture, and Compliance with Unified Network Monitoring
- Cisco ASA - Firepower Articles
- Configuring Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco Routers
- Configuring Point-to-Point GRE VPN Tunnels - Unprotected GRE & Protected GRE over IPSec Tunnels
- Configuring IPSec VPN between Palo Alto Firewall & Meraki MX Security Appliance
Explore a Comprehensive Enterprise-Grade Hybrid Infrastructure Monitoring Platform
Why VPN Tunnels Commonly Experience Issues
VPN tunnels, particularly IPsec-based site-to-site tunnels, rely on multiple tightly coupled components working in precise alignment. Any inconsistency across encryption settings, authentication methods, routing policies, or WAN conditions can result in tunnel instability, partial connectivity, or complete failure.
Configuration mismatches remain one of the most frequent causes of VPN issues. Encryption algorithms, hashing methods, Diffie-Hellman groups, and security association lifetimes (SA) must match exactly on both tunnel endpoints. These mismatches are often introduced unintentionally during firewall policy updates, platform migrations, or firmware upgrades.
WAN-related conditions such as packet loss, latency, jitter, or ISP link congestion also contribute significantly to VPN instability. These issues tend to appear during peak usage periods and may resolve without intervention, making them difficult to diagnose without continuous monitoring and historical trend analysis.
Routing changes further complicate VPN reliability. Incorrect static routes, dynamic routing advertisements, or policy-based routing rules can redirect traffic away from the tunnel. In such cases, the VPN may appear operational while applications silently fail to communicate.
VPN Tunnel Parameters That Should Be Monitored
AIOps for Modern IT Operations: Automating Monitoring, Reducing Noise, and Preventing Outages
 The days of relying solely on static monitoring dashboards and manual firefighting are long gone. Today’s environments demand automation-first operations, real-time observability across every layer, and AI-driven intelligence that can make sense of the massive volume of telemetry and logs modern systems generate.
The days of relying solely on static monitoring dashboards and manual firefighting are long gone. Today’s environments demand automation-first operations, real-time observability across every layer, and AI-driven intelligence that can make sense of the massive volume of telemetry and logs modern systems generate.
With organizations accelerating their move to cloud-native architectures, virtualization, edge computing, and hybrid infrastructures, IT operations teams now manage ecosystems that are more distributed, interconnected, and unpredictable than ever before. Traditional tools simply can’t keep up with the scale or speed.
This is exactly where AIOps is redefining the game. By combining machine learning, advanced analytics, and automated remediation, AIOps empowers IT teams to detect anomalies earlier, correlate events across domains, and resolve issues proactively—long before users feel the impact. For technical teams, it’s not just an upgrade; it’s a fundamental shift in how operations are executed, optimized, and scaled.
Key Topics
- The Evolution of IT Operations – From Reactive Monitoring to Intelligent Automation
- How Does AIOps make it all easier?
- How Modern IT Challenges Push Teams toward Unified Monitoring
- Alert Noise
- Limited Visibility Across Tools
- Slow MTTR (Mean Time to Resolve)
- Fast-paced, Constantly Changing Environments
- Where OpManager Plus Fits in this AIOps Era
- The Benefits of a Unified, AIOps-Powered Platform
- End-to-end Visibility
- Reduced Noise
- Faster Incident Resolution
- Operational Efficiency
- Future Readiness
- Summary
Download your copy of OpManager Plus Now
The Evolution of IT Operations - From Reactive Monitoring to Intelligent Automation
In the early days of IT, operations were largely reactive. IT teams would wait for a system to fail—whether it was a server crash, network outage, or application hiccup—and scramble to fix the issue. As technology advanced, the industry shifted towards more proactive approaches. Monitoring tools emerged to detect problems before they escalated, but as IT environments grew in complexity, so did the landscape of tools. Each tool specialized in a different layer: one focused on the network, another on servers, and yet another on applications. This specialization, while useful, led to tool sprawl—multiple disparate solutions with siloed data, leaving IT teams with fragmented insights. Worse, there was no unified system to correlate these insights, resulting in a disjointed view of the infrastructure.
The result? Longer Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) as teams struggled to connect the dots between alerts and incidents.
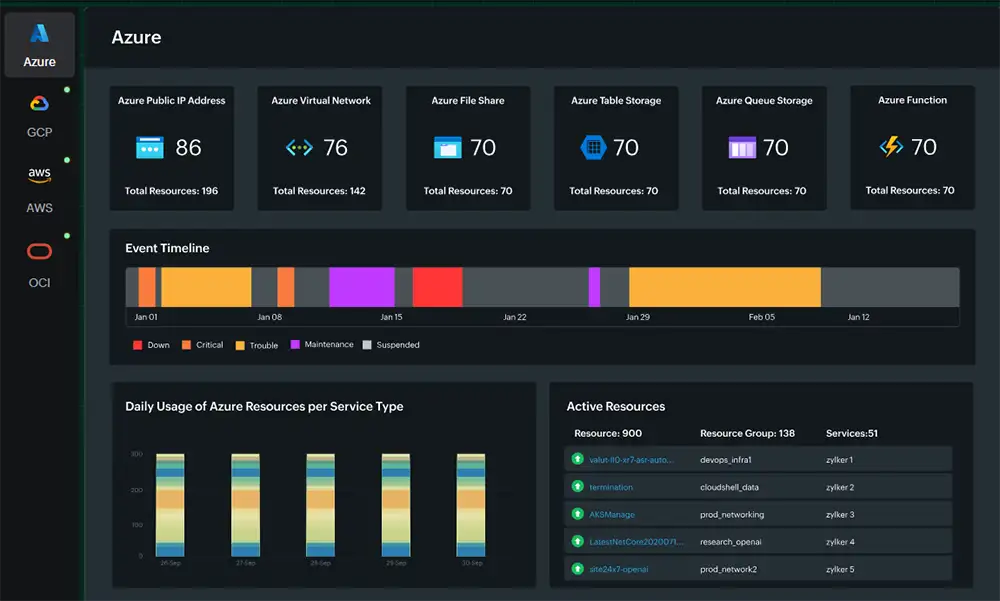
Proactive IT Excellence: How Unified IT Monitoring Tool Transforms Hybrid Cloud Environments
Introduction: Why Unified IT Monitoring Matters More Than Ever
 The modern IT landscape is more complex than ever before. Organizations operate across a mix of on-premises systems, private clouds, and public cloud platforms—a dynamic ecosystem known as the hybrid cloud environment. While this model enables flexibility and scalability, it also creates challenges: managing distributed infrastructures, ensuring consistent uptime, and protecting systems from performance degradation or security incidents.
The modern IT landscape is more complex than ever before. Organizations operate across a mix of on-premises systems, private clouds, and public cloud platforms—a dynamic ecosystem known as the hybrid cloud environment. While this model enables flexibility and scalability, it also creates challenges: managing distributed infrastructures, ensuring consistent uptime, and protecting systems from performance degradation or security incidents.
Traditional monitoring tools, designed for single environments, can’t keep pace. Downtime or slow response times across just one node can disrupt entire business operations, leading to lost revenue and customer dissatisfaction. That’s why companies are shifting toward unified observability platforms—comprehensive solutions that bring all monitoring data into a single, intelligent interface.
Related Articles:
- Boost Firewall Security with Automation: Compliance, Vulnerability, Validation & Real-Time Control
- Enhance Firewall Performance, Security Posture, and Compliance with Unified Network Monitoring
The Rising Complexity of Hybrid IT Environments
Modern IT teams juggle applications running on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud alongside legacy systems hosted in local data centers. Each component generates massive amounts of telemetry data, logs, and metrics. Without a unified IT monitoring tool for hybrid cloud environments, this information becomes fragmented, making it nearly impossible to gain real-time situational awareness.
Test drive the worlds best unified IT monitoring tool for hybrid cloud environments
From Reactive to Proactive: The Shift Toward Unified Observability Platforms
Reactive monitoring—responding after a system fails—is no longer acceptable. Organizations now demand proactive IT monitoring that predicts issues before they impact users. A unified monitoring platform powered by AI insights enables IT operations and DevOps teams to anticipate performance anomalies, automate remediation, and maintain uninterrupted service delivery.
Meet Site24x7: A Cloud-Native, Unified Monitoring Solution for Modern IT Operations
Overview: What Is Site24x7?
Site24x7, developed by Zoho Corporation’s ManageEngine division, is a cloud-native, all-in-one IT monitoring and observability platform designed for IT operations, DevOps engineers, and site reliability teams. Built to scale from startups to global enterprises, it monitors over 1,000 technologies, spanning servers, websites, networks, applications, and containers.
Enhance Firewall Performance, Security Posture, and Compliance with Unified Network Monitoring
 As modern networks become increasingly complex, maintaining strong firewall performance, ensuring a robust security posture, and meeting growing compliance requirements have become top priorities for IT teams worldwide. Traditional firewalls, while essential for blocking cyber threats, often lack the unified visibility and real-time analytics needed to manage today’s hybrid, cloud-driven, and highly distributed infrastructures.
As modern networks become increasingly complex, maintaining strong firewall performance, ensuring a robust security posture, and meeting growing compliance requirements have become top priorities for IT teams worldwide. Traditional firewalls, while essential for blocking cyber threats, often lack the unified visibility and real-time analytics needed to manage today’s hybrid, cloud-driven, and highly distributed infrastructures.
In this article, we’ll explore the challenges of managing firewall performance and compliance in modern networks, explain why unified monitoring is essential, and show how platforms like Site24x7 can help streamline security, boost efficiency, and strengthen overall network resilience.
Key Topics
- Why Firewalls Alone Aren’t Enough for Network Security
- Key Challenges in Managing Firewall Performance
- Why Unified Network Monitoring is Essential
- How Site24x7 Strengthens Firewall Performance and Compliance
- Real-Time Firewall Performance Monitoring with SNMP
- Automating Configuration Backups and Compliance Enforcement
- Firmware Vulnerability Tracking and Risk Mitigation
- Achieve a Stronger Security Posture with Site24x7
- Summary
Boost your Network’s Security and Performance with AI driven Unified Network Monitoring
Why Firewalls Alone Aren’t Enough for Network Security
Security breaches rarely result from the absence of firewalls. More often, they occur due to misconfigured firewall rules, resource bottlenecks, or blind spots caused by fragmented monitoring tools. Even if a firewall blocks malicious traffic, it can still introduce network latency, drop critical sessions, or fail to meet stringent compliance mandates if performance and configurations are not continuously monitored.
This is where Unified Network Monitoring becomes critical. By consolidating network security monitoring, performance analytics, and configuration management into a single platform, organizations gain full visibility across their IT infrastructure. With the right solution, IT teams can proactively detect issues, enforce security policies, automate compliance checks, and optimize firewall performance across all locations—without relying on disconnected dashboards or manual processes.
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!
Featured Categories:
Top Picks:
Palo Alto Firewall Configuration Options. Tap Mod…
Free Webinar: Enterprise-Grade Security and Manag…
Introduction to Palo Alto Next-Generation Network…
Understanding Deduplication. Complete Guide to De…
WAN Optimization vs SD WAN Networks. Today’s Challenges & Difficulties for WAN Optimization
The Need for a Converged SASE Platform. Converging Network & Security Services with Catonetworks SASE Platform
Understanding Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and how it integrates with SD-WAN
Check Point Software and Cato Networks Co-Founder Shlomo Kramer Shares His Journey: From ‘Firewall-1’ Software to Today’s Firewall as a Service

The VLAN Concept - Introduction to VLANs

VLANs - Access & Trunk Links

InterVLAN Routing - Routing between VLAN Networks

Comparing Traditional Flat & VLAN Networks
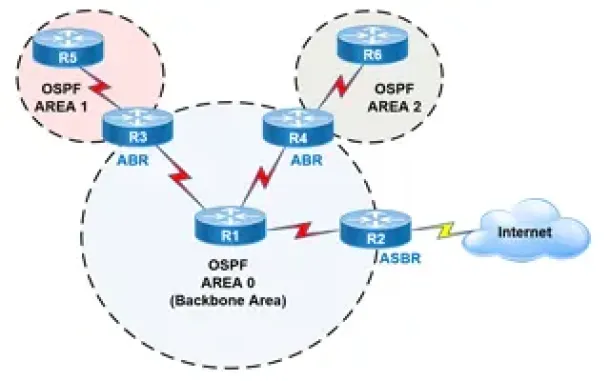
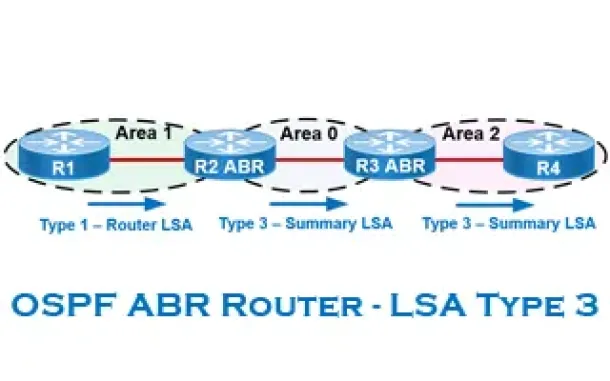
OSPF - Part 2: How OSPF Protocol Works & Basic Concepts: OSPF Neighbor, Topology & Routing Table, OSPF Areas & Router Roles, Theory & Overview
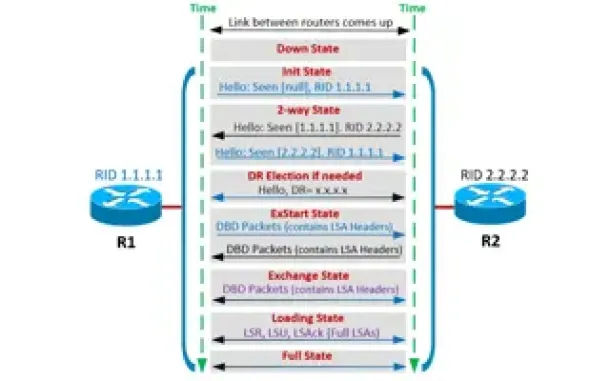
OSPF - Part 4: OSPF Neighbor States – OSPF Neighbor Forming Process

The IP Routing Process - Step-by-Step Analysis