VPN For Torrenting, P2P and File Sharing. Test Anonymous Torrenting, Avoid Bandwidth Throttling, Protect Your Identity
 The word torrenting is often viewed as synonymous with pirating. It’s seen as a shady and illegal practice, used to con hard working artists out of their money. As a result, internet service providers often blanket ban torrent websites or severely throttle downloads. If you aren’t using a VPN for torrenting, there’s a good chance you’re affected by this. However, ISPs over-arching policies can hurt users that use Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file sharing for innocent purposes.
The word torrenting is often viewed as synonymous with pirating. It’s seen as a shady and illegal practice, used to con hard working artists out of their money. As a result, internet service providers often blanket ban torrent websites or severely throttle downloads. If you aren’t using a VPN for torrenting, there’s a good chance you’re affected by this. However, ISPs over-arching policies can hurt users that use Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file sharing for innocent purposes.
How Torrenting & Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Works
Instead of using dedicated servers, P2P utilizes the connections of other users to distribute files. As they download a torrent, the individual also uploads a small portion for others to download. This creates an interconnected network where files are provided by many different people.
One huge example of legal P2P usage is gaming. Online games such as World of Warcraft, League of Legends, and downloads from UPlay all have a P2P option. This saves on server costs for the developers and can increase torrent speed. This can foster development for smaller, indie companies, who might not have the infrastructure for lots of servers.
Download Torrents Safely & Bypass any geo-location restrictions using StrongVPN Client
In fact, Windows 10 even takes advantage of this method to save on bandwidth issues. The OS delivers updates in multiple parts, pulling bits from both PCs on the same network, over the internet, and Microsoft’s own data centers. This feature is turned on by default since the Windows 10 Anniversary Update in the summer of 2016.
However, more important is the role of torrenting in distributing public data. The Internet Archive caches huge amounts of websites and offers a huge variety of public domain books, TV shows, and audio recordings. The non-profit recommends the use of torrents to download its content, as it saves on bandwidth and allows it to continue its vital work.
This role extends even to government. NASA has used torrents several times in the past to distribute its findings, including this high-resolution picture of earth. The UK government has done similarly, releasing large datasets on public spending via BitTorrent.
As well as supporting government, BitTorrent is also used to oppose it. Transparency sites such as Julian Assange’s Wikileaks often release so-called ‘insurance files’ through torrents. Shortly before the leak of Hilary Clinton’s emails, the site published an 88GB, 256-AES encrypted file. This keeps the organization from being shut down – if WikiLeaks goes dark, an automated message sends out an unlock password for all the data. In previous cases, files have reached upwards of 400GB.
Despite the genuine uses of P2P, users still get attacked by copyright claimants, sometimes inaccurately. In 2015, the creators of B-movie Elf Man filed a lawsuit against hundreds of users who claimed to have never even heard of the movie. Ryan Lamberson was one of these defendants and was eventually reimbursed for $100,000 in legal fees. Closer examination of evidence revealed that the tools used by the copyright holder did not account for several shortcomings, and only tracked uploads rather than downloads.
The defense also pointed out that the primary evidence was little more than an IP address. This information came from a third-party software that connected to the BitTorrent swarm in which the files were shared. However, some torrent software allows for the spoofing of IP addresses, and the investigator failed to account for several other false positives. Because of the win, several other Elf Man cases were dropped or settled for a lower value.
Other thrown cases include the Adam Sandler movie The Cobbler, and a 53-year-old artist painter was wrongly accused of illegally downloading and sharing 18 films and TV shows. Thankfully, there is a simple way to avoid such risks.
Anonymous Torrenting with a VPN Service
Using a VPN for torrenting will ensure your identity remains private, not just from ISPs, but copyright claimants and government. When you connect to a VPN, all your traffic goes through a “tunnel”. The individual packets that make up your data contain information such as IP Address, protocol, and other identifying information.
Tunneling wraps those packets in others that provide extra security against prying eyes. In addition, the data is encrypted in transit, meaning ISPs, service providers and other middlemen see nothing but gibberish. Different providers use different encryption methods, the most common being IPSec, L2TP, and OpenVPN.
The benefit of this tunneling is clear. An ISP or copyright holder can only see the IP address of the VPN servers, not your own. This makes for anonymous torrenting, and they can’t see what website’s you’ve visited either. Though this might not protect you against entirely baseless accusations, it should stop you from coming under genuine suspicion.
A VPN for torrenting will also provide you with protection in other ways. To stay safe on public WiFi, they are almost essential. Without one, attackers can snoop on your online traffic, possibly recovering passwords and credit card details. You could also be vulnerable to malware on your machine and tracking from third parties.
However, not all VPNs are created equal. Though some provide anonymous torrenting and public WiFi protection, others are questionable at best. Researching hundreds of different providers can be a pain, so instead we’ve done that for you. Our network security team has produced a VPN service review of all the Best VPN Service Providers, alongside detailed feature lists.
Finally, our Begineers Guide to VPNs article aims to educate users with all the necessary information so they can fully understand how a VPN works, security features offered by the best VPN service providers, what to look for in a VPN and what to stay away from.
Avoid ISP Bandwidth Throttling
 Encrypted communication has the add-on effect of avoiding bandwidth throttling from ISPs. As mentioned earlier, service providers inspect packets to classify different data. This lets them put a speed cap on specific mediums. This is usually done unofficially and some service providers will deny the practice despite significant data to the contrary.
Encrypted communication has the add-on effect of avoiding bandwidth throttling from ISPs. As mentioned earlier, service providers inspect packets to classify different data. This lets them put a speed cap on specific mediums. This is usually done unofficially and some service providers will deny the practice despite significant data to the contrary.
Despite this, it’s becoming more and more routine for ISPs to throttle or block torrent downloads. Everything you receive goes through their servers, allowing them to analyse it with Deep Packet Inspection. This method lets the service provider look at different data packets and classify it into different categories, such as video, music, and torrents.
Bandwidth throttling can be achieved in several ways. One method is blocking router ports often used for BitTorrent. Typically, P2P downloads go through TCP ports from 6881-6889. By limiting the speed on these, an ISP can cut out a big chunk of bandwidth.
However, this method is becoming less and less popular. Increasingly, torrent clients randomize TCP ports or tell users if there are any issues. As a result, internet service providers use methods that are harder to dodge.
One such technique is called traffic shaping. The flow of certain packets is delayed in favour of others, affecting download and upload speed. This can be done as a blanket, or through intelligent burst shaping. Burst shaping increases torrent speeds for a short period, before gradually returning to a lesser speed. Thus, extended downloads such as movies, games, and streaming are slower, while web pages still load quickly.
The need for shaping comes from the limited bandwidth resources of an ISP. It lets the service provider guarantee performance to other users by reducing the effect of heavy users. Often, P2P is main target for this, and it’s easy to see why. Torrent downloads use large amounts of bandwidth and therefore cost a lot of money to sustain. In addition, companies are under a lot of legal pressure from copyright holders. By throttling, they can assure the parties that they’re doing their bit to limit the impact of pirates.
Unfortunately, it’s difficult to differentiate between legal P2P downloads and illegal ones. This means that regular users can be throttled due to blanket policies. You can check if your torrents are being throttled by running the Glasnost test (no longer developed). The eight-minute download will detect bandwidth throttling in the upload and download streams separately.
We tried the Glasnost test which failed to confirm our suspicions of BitTorrent bandwidth throttling:
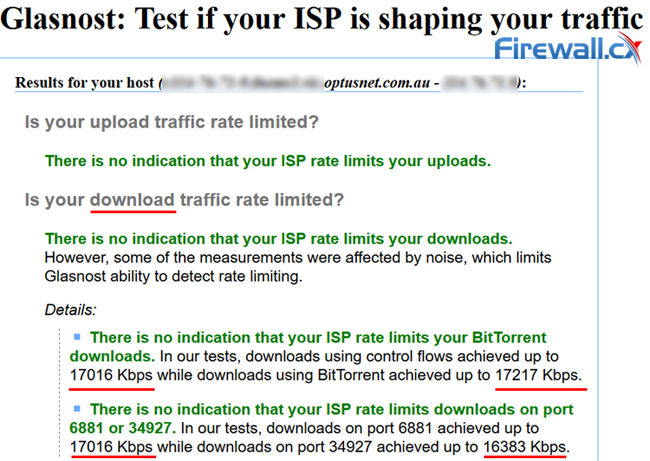
Glasnost failed to detect any BitTorrent Bandwidth Throttling for our connection
There are many cases where the Glasnost test will not accurately detect BitTorrent bandwidth throttling which is where personal experience confirms these suspicions.
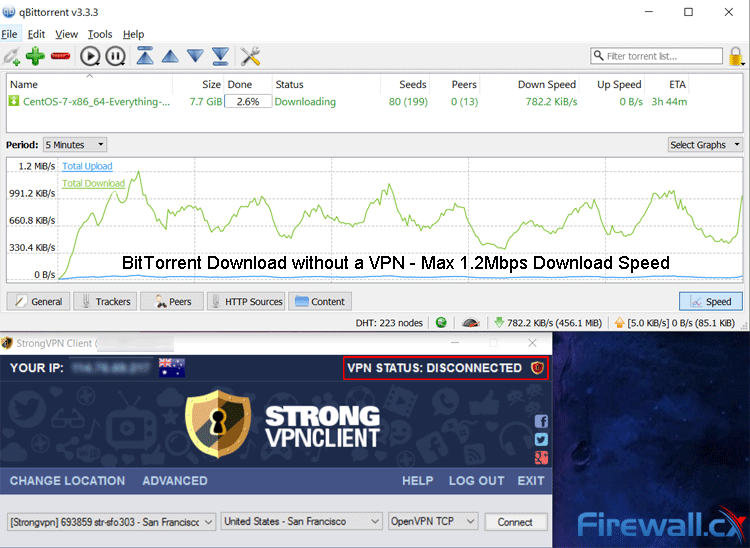
BitTorrent without a VPN provided a Max Download Speed of 1.2Mbps
If you find an issue with your broadband provider, there are still steps you can take avoid throttling. Using a VPN for torrenting will ensure your ISP can’t categorize that data. If they don’t know it’s happening, they probably won’t throttle it, which will result in faster speeds.
How a VPN Can Increase Torrent Speeds – Real Example Avoiding BitTorrent Bandwidth Throttling
VPN speed increases are often quite significant. The exact difference depends on your ISP, but it can increase torrent speeds by double or triple. This is despite latency caused by encryption methods and cross-continent connections.
In our tests, we found an increase in BitTorrent download speed from a pitty 1.3 Mbps max to a whopping 3.1 Mbps max using our StrongVPN connection. This test was carried out on a completely legal download of CentOS, showing that ISPs don’t make exceptions. This reduced the ETA of the download significantly, bringing it to an acceptable time.
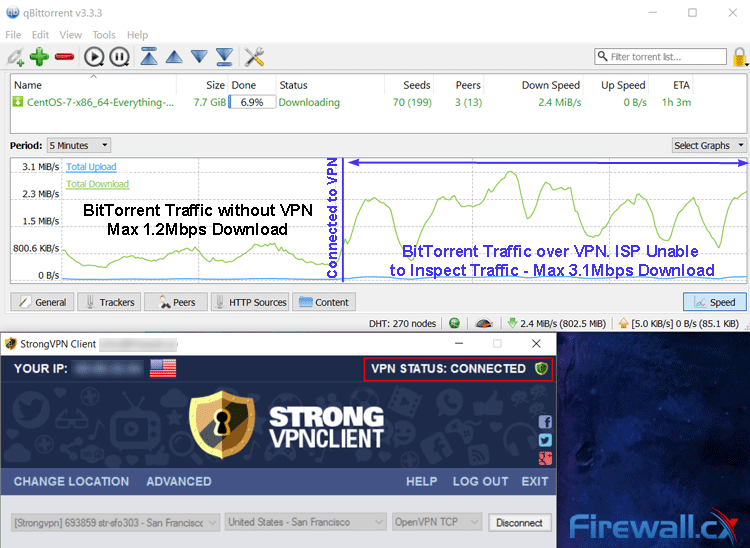
BitTorrent traffic over VPN with StrongVPN increased out download speeds by almost 3 times
It’s worth noting that using a VPN for torrenting doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll get the full speed of your internet connection. The speed upon which you can download is dependent on many factors including the plan you have with your ISP, how busy your local ISPs exchange is, VPN provider & VPN server you’ve connected to, their (VPN servers) max upload bandwidth, type of encryption selected for the VPN and many more.
For example, torrenting on stronger, 256-AES encryption, results in a slower connection than 128-AES encryption. The latter also provides less protection (weaker encryption), so the best fit depends on your usage scenario. The type of data authentication also makes a difference. Data protection prevents so-called active attacks, where the attacker gets between you and the VPN server and inject or modify data. SHA1 is the fastest method, but SHA256 is also common. It’s worth checking what options there are before you buy a VPN for torrenting.
Ensuring Your VPN for Torrenting is Protecting You
Despite these protection methods, you still may not be safe torrenting on certain VPNs. Some providers have strict policies on P2P downloads, often due to their legal situation of location. Many do not officially support illegal activity and if your provider keeps logs, they may be forced to hand them over to authorities or copyright holders.
A free VPN for torrenting is especially risky. Fighting copyright holders takes a lot of time and resources, and most companies will only protect paying customers. They can also come with data caps or sell your details, so it’s usually worth paying a small monthly fee for true anonymous torrenting.
Paid services have a vested interest in keeping consumers safe from copyright holders. As a business, their reputation depends on delivering what is advertised and keeping users safe. It’s always worth checking the provider’s policies before signing up.
However, there are also issues that can stem from the individual user, rather than the VPN provider. Your IP address may be revealed through a DNS Leak or other means. This is easy to check and can be done straight from your browser.
One of the most popular online tools ipMagnet. First, you will want to visit the site with your VPN. Loading the web page should display the IP address assigned by your VPN provider, not the IP address assigned by your ISP. Once this has been verified, you’ll want to hit the blue Magnet link text shown below:
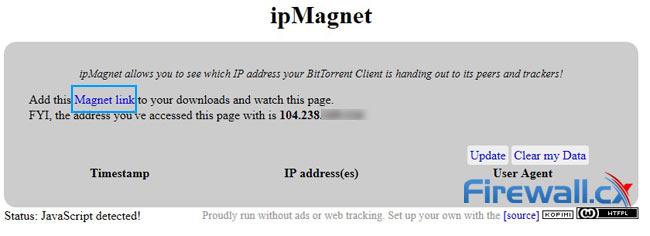
ipMagnet allows BitTorrent users verify they are not exposing their real IP address
You will then be prompted to add the file to the BitTorrent application of your choice. The link points to a fake file, and the embedded tracker is controlled by qMagnet who archives the information and returns it to you. The download is completely legal and the files shouldn’t take up any space on your hard drive. Moreover, the source code of ipMagnet is freely available online. It’s best to let this run for a while until multiple lines show in the table:
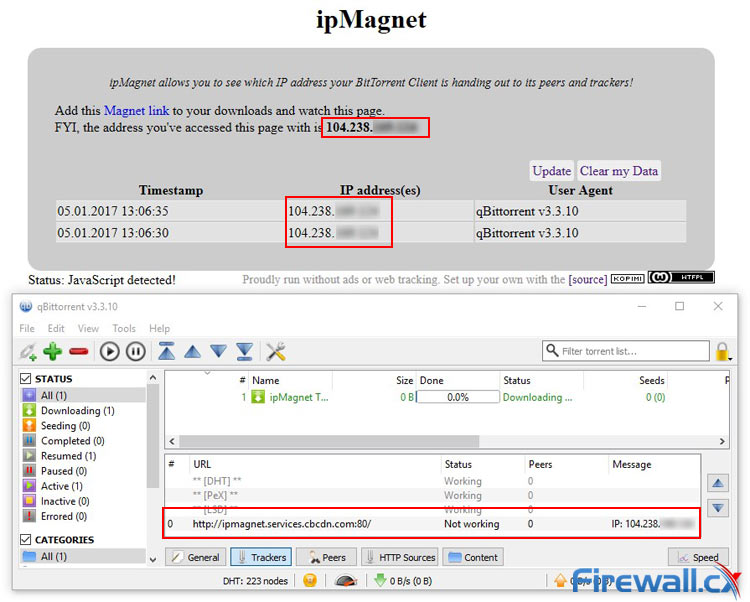
ipMagnet in Action reveals our VPN Service Provider is not exposing our real IP address
You can also use see the IP address under the trackers section of your BitTorrent client. The message field should only display the IP address shows in your VPN client and will be updated if anything changes. If any of them display your real IP address (assigned by your ISP) you have a problem. This means that your real IP address is leaking and is viewable to your peers and snoopers.
The best way to avoid such leaks is through a Kill Switch. This feature is often found within reliable VPN service providers or BitTorrent clients and shuts off your connection if the VPN for torrenting drops out. With reliable providers, this doesn’t happen often, but a few seconds is all it takes to expose your identity.
Set Up a VPN Kill Switch in qBittorrent
Some torrent clients have Kill Switch functionality built-in. This is true for popular providers such as qBitorrent, Vuze, and uTorrent and can help enforce anonymous torrenting. You can follow this guide to enable it for qBittorrent in Windows 10:
- Hit the Windows key and type Network and Sharing Center. Press Enter.
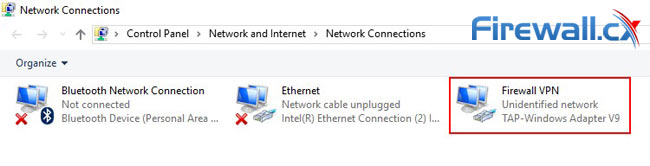
- Click Change adapter settings in the left side panel.
- In the Network Connections window, identify the adapter your VPN uses. For us, it was an Ethernet TAP-Windows Adapter you can see as Firewall VPN:
- Open qBittorrent on your system.
- Select Tools > Options. Click the Advanced tab.
- In the Setting column, look for Network Interface.
- Set the drop down menu tothe previously identified adapter (Firewall VPN).
- Click OK.
- Restart qBittorrent.
Note that you need to fully quit qBittorent for this to work. That means right-clicking on the icon in the system tray and clicking exit. On start, you should notice that your download speed won’t budge from zero unless you enable your VPN. As soon as you start it up again, you’ll see an increased torrent speed.
Set Up a VPN Killswitch With Comodo Firewall
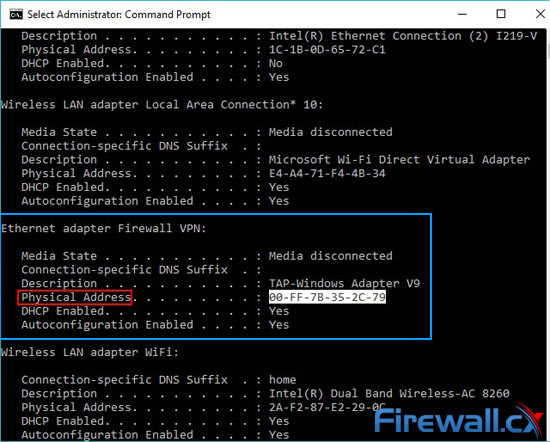
If neither your VPN or torrent client works with a Kill Switch, you’ll have to look elsewhere. Comodo Firewall is a good, tried and tested alternative. The setup is more complex, but ensures stable privacy and less fiddling later. First, you need to find the VPNs physical address. To start, type cmd in the start menu and run it as an administrator.
Then type ipconfig /all and look for the adapter that says TAP -Windows Adapter next to the description field. Note down the Physical Address, and start Comodo Firewall:
You’ll then want to set up a new network zone. Go to Settings > Firewall > Network Zones and select Add > New Network Zone. Name it VPN for Torrenting and press okay.
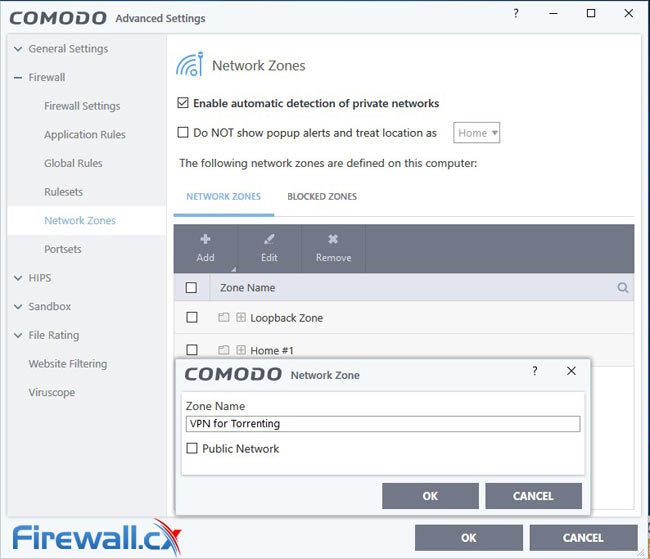
Your new zone should now show up in Comodo. Select it and click Add > New Address. Change the type to Mac Address and input the physical address from earlier:
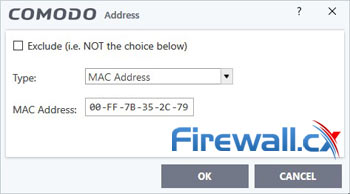
Now you’ll want to create some rulesets. Go to Firewall > Rulesets and hit Add. Name it Kill Switch Ruleset. You can then add three separate rulesets with the following settings:
- Action: Block
- Protocol: IP
- Direction: In or Out
- Source Address: Any Address
- Destination Address: Any Address
- Action: Allow
- Protocol: IP
- Direction: Out
- Source Address: Network Zone/VPN for Torrenting
- Destination Address: Any Address
- Action: Allow
- Protocol: IP
- Direction: In
- Source Address: Any Address
- Destination Address: Network Zone/VPN for Torrenting
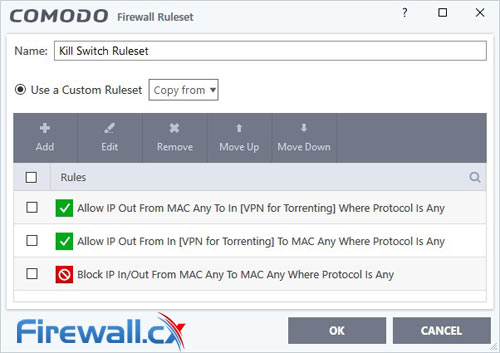
Hit OK and you’re almost done. In the Application Rules section of Advanced Settings, you can add any application you want the Kill Switch Ruleset to apply to. In this case, we want to add our torrent client. Browse to the location of the program and add it to the rule. Finally, check Use Ruleset and select Kill Switch Ruleset.
By using one or all the methods, you will ensure your VPN doesn’t leak your identity when it goes down. To be certain, run another test on ipMagnet with your VPN enabled and disabled. No IPs should appear when you aren’t connected.
VPN Port Forwarding & NAT Firewalls
Unfortunately, some users will still have problems downloading torrents with a VPN enabled. This is usually due to the use of VPN NAT firewalls. VPN usage degrades the protection of the NAT firewall built into your router. The functionality blocks incoming traffic unless it’s in response to a request you made. However, the encrypted nature of VPN tunneling means you lose that protection.
As a result, most VPN providers set up their own NAT firewalls that sit between their servers and the internet. This feature is usually presented as an optional toggle and offers much of the same protection. It can also result in issues when you’re using a VPN for torrenting.
NAT firewalls can make your connection slower, offsetting much of the anti-throttling advantages. To avoid this, you’ll have to set up a port in the firewall that lets P2P traffic through. This is generally called VPN port forwarding.
Some VPN port forwarding can be reached from the settings menu. A simple toggle is usually enough to solve any issues, but naturally, this can reduce security slightly.
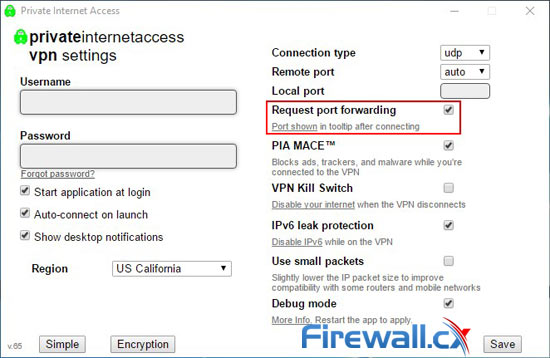
VPN Port Forwarding in Private Internet Access
To get maximum efficiency, you will want port forward via the torrent client too. qBittorrent and other clients enable NAT-PNP and UPnP by default, which automates the process. In other scenarios, you may have to manually input the port in your torrent client. The five-digit port number usually displays on connection or inside the VPN window.
If your provider doesn’t provide you with a VPN port forwarding number or settings toggle, it’s worth contacting directly via email. Sometimes the ports will be provided on request rather than to everyone. In other cases the provider port forwards by default, but doesn’t inform the user.
Summary
All the aforementioned methods will help keep your identity and wallet protected. In the case of Torrent throttling, you will be one step closer to getting the connection speeds you pay for. Moreover, careful application will make it impossible for anyone to verify your identity and hand out hefty fines.
Despite this, using a VPN for torrenting doesn’t mean you’re completely immune. Some ISPs will throttle all encrypted traffic, or target individual users who use a lot of bandwidth. The failure of Kill Switches can also give you away, though they happen very rarely. Port forwarding can cause issues on occasion, making you more vulnerable to other kinds of attacks.
Finally, the precautions are next to useless if you don’t choose a trusted and logless VPN provider in the first place. As the market grows it's becoming increasingly important to find the Best VPN Service Provider for you through reliable VPN service reviews. If you use P2P file sharing, that’s a company who supports those methods and won’t hand over your IP to third parties.
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!














