Differences Between VMware vSphere, vCenter, ESXi Free vs ESXi Paid, Workstation Player & Pro
 In this article we will cover the differences between VMware ESXi, vSphere and vCenter while also explain the features supported by each vSphere edition: vSphere Standard, Enterprise plus and Plantium edition. We will touch on the differences and limitations between VMware Workstation Player and VMware Workstation Pro, and also compare them with EXSi Free and EXSi Paid editions.
In this article we will cover the differences between VMware ESXi, vSphere and vCenter while also explain the features supported by each vSphere edition: vSphere Standard, Enterprise plus and Plantium edition. We will touch on the differences and limitations between VMware Workstation Player and VMware Workstation Pro, and also compare them with EXSi Free and EXSi Paid editions.
Finally we will demystify the role of vCenter and the additional features it provides to a VMware infrastructure.
Key Topics:
- Difference between VMware vSphere and vCenter
- What is VMware ESXi?
- Difference Between VMware ESXi Free and ESXi Paid Version
- When Do You Need vCenter?
- Difference Between VMware Workstation Player and VMware Workstation Pro
- Summary
Visit our Virtualization and Backup section for more high-quality technical articles.
Concerned about your VM machines and data? Download now your Free Enterprise-grade VM Backup solution
Related Articles:
- 6 Key Areas to Consider When Selecting a VM Backup Solution
- Understanding Deduplication. Complete Guide to Deduplication Methods & Their Impact on Storage and VM Backups
- How to Fix VMware ESXi Virtual Machine 'Invalid Status'
- How to Enable SNMP on VMware ESXi Host & Configure ESXi Firewall to Allow or Block Access to the SNMP Service
- How to Enable or Disable SSH on VMware ESXi via Web GUI, vSphere Web GUI (vCenter), vSphere Client and Shell Console
Difference Between VMware vSphere & vCenter
It’s sometimes difficult to keep up to date with the latest names of software. Even the largest technology vendors change their product names from time to time. Unfortunately, getting the product name wrong can result in various costly consequences including purchasing the wrong product or an older version with differentiating feature sets.
Contrary to popular belief, vSphere and vCenter are actually different products:
- vSphere is VMware’s name for a suite of Infrastructure products. You can think of it as a platform name which includes lots of different components.
- vCenter is the name of one of the components under the vSphere suite. vCenter runs on a Windows Server VM and provides the management and control plane of the entire VMware environment. This is also shown in the diagram below:
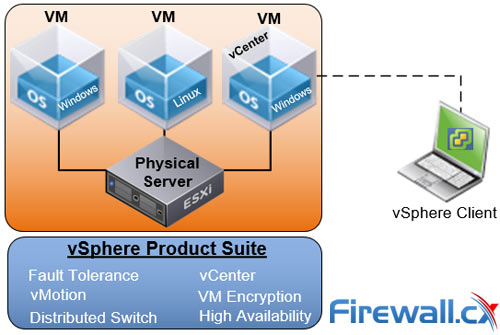
Looking at the vSphere suite, the components and features that vSphere includes depend on your licenses. vCenter Server is available on all vSphere editions.
Here is an overview of some features for the main vSphere editions:
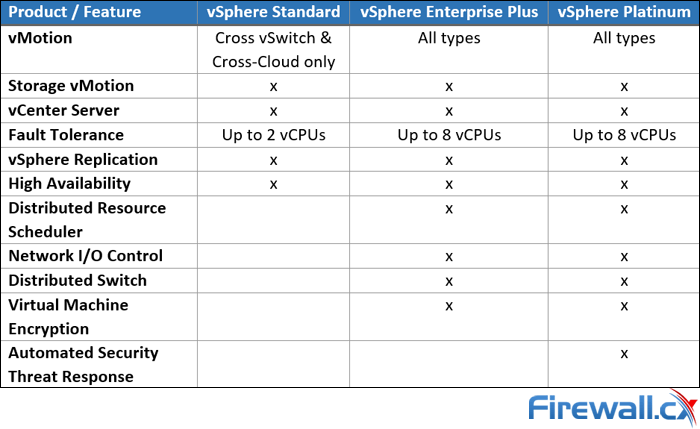 You will notice that this vSphere feature table contains many different technologies which are found in different VMware software components.
You will notice that this vSphere feature table contains many different technologies which are found in different VMware software components.
vCenter is a management tool that helps manage multiple ESXi / vSphere Hypervisors within the datacentre. Earlier versions of vCenter (also known as vCenter Server) ran exclusively on Windows Server (shown in the previous diagram) whereas now VMware now offers the vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) which runs on either SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 64-bit (vCSA v6.0) or VMware’s proprietary Photon OS (vCSA v6.5 and above).
You log in to vCenter Server via an HTML5 browser (formally a Flash client) which looks like this:

From here, we can manage all vSphere related components (and their corresponding features) which include:
- vCenter Server (vCSA)
- vSphere Hypervisors (ESXi Servers)
- vSphere Update Manager
- vSphere Replication
So, in summary, the difference between vSphere and vCenter is that vSphere consists of a suite of VMware components with vCenter Server being one of those.
vCenter Server is the management software or if you prefer, tool, to help manage your vSphere Components and all their features.
You can use some vSphere components without a vCenter Server but some features will not be available.
What is VMware ESXi?
ESXi is a Type-1 Hypervisor which means it’s a piece of software that runs directly on a bare-metal server without the requirement of an operating system. As a Hypervisor, ESXi manages access to all physical resources such as CPUs, memory, network interface cards, storage (HDD, SSDs etc) and other.
ESXi’s vmkernel sits between the virtual machines and physical hardware and from there it shares the available hardware including CPUs, storage (HDDs, SSDs etc), memory and network interfaces of the physical host amongst the multiple virtual machines. Applications running in virtual machines can access these resources without direct access to the underlying hardware.
Vmkernel is the core software responsible of receiving requests from virtual machines for resources and presenting the requests to the physical hardware.
There are stricter compatibility requirements for ESXi installations as hardware drivers need to be certified. However once ESXi is installed and operational, you get access to Enterprise-grade Virtual Machines features.
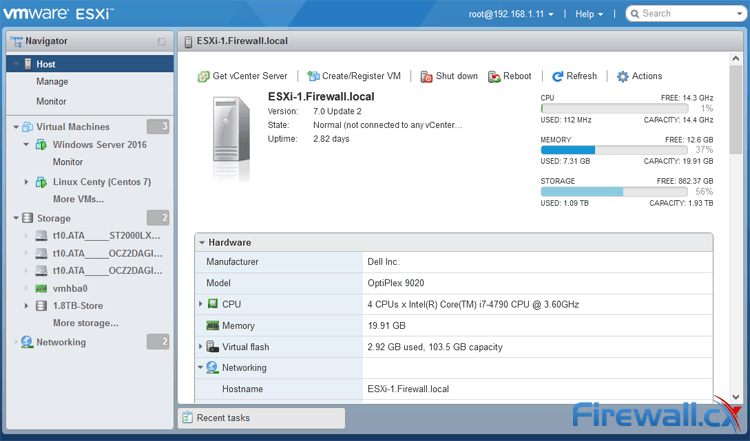 VMware ESXi GUI Interface - Click to enlarge
VMware ESXi GUI Interface - Click to enlarge
VMware ESXi comes in a variety of flavours. A free version exists if you simply need to deploy basic Virtual Machines with no High Availability or central management requirements. This is best suited for trialling software and labs which are not in production.
For mission-critical applications, you should consider the paid version of ESXi which comes with VMware support and features geared toward professional environments. Add on VMware’s vCenter Server enable central management all of your ESXi servers and take your datacentre one step further with features such as:
- Clustering
- High Availability
- Fault Tolerance
- Distributed Resource Scheduler
- Virtual Machine Encryption
Difference Between VMware ESXi Free & ESXi Paid Version
The VMware ESXi free vs ESXi paid debate comes up a lot, but fortunately, it is easily answered.
The question to ask yourself is if you are planning to run mission-critical applications on top of ESXi. By mission-critical we mean applications that your business depends on. If the answer is yes, then you will require the paid version of ESXi with support so that you can contact VMware should anything go wrong.
Even if the answer is no, you might still consider a paid version of ESXi if you need the management functions of vCenter Server. Such use cases might be large development companies who don’t consider their test and development environments mission-critical but they do want a way to manage hundreds or thousands of Virtual Machines.
VMware ESXi free is still feature-rich though. Therefore for a small environment where your business won’t grind to a halt if an ESXi server goes offline, might be cost-effective even with additional manual management tasks to conduct. Keep in mind though that backup features will not be available in the free version, meaning that native backup via ESXi won’t be possible. You can work around this by installing and managing backup agents within your operating systems. This is one example of management overhead that you wouldn’t have with a paid version.
When Do You Need vCenter?
It’s worth keeping in mind that even with a paid version of ESXi, you will still need a vCenter Server license to use any clustering features. A paid version of ESXi does offer some benefits (such as VADP backup abilities) but without a vCenter Server license, most of the benefits are not available.
Almost all customers of paid ESXi licenses will also purchase a vCenter Server license so that those licenses ESXi servers can be centrally managed. Once all ESXi servers are managed by vCenter Server, you unlock all the ESXi features that you are licensed for.
So when do you need a vCenter Server? The answer is simple. To unlock features such as Clustering, High Availability (an automatic reboot of VMs on a failed host to a healthy host), Cloning and Fault Tolerance. If you are looking to add other VMware solutions to the datacentre including vSAN, vSphere Replication or Site Recovery Manager, then all of those solutions require access to a vCenter Server.
In summary, if you find that you need the paid ESXi version then you are most likely also going to need a vCenter Server license too. Fortunately, VMware provides discounted Essentials and Essentials Plus bundles with a 3 host (physical servers) limit, these bundles include ESXi and a vCenter server license at a discounted rate to keep initial costs down.
Just by looking at the vSphere Client can you see the various vCenter related options which show the value added by bolting on vCenter to your stack of management software for your datacentre:
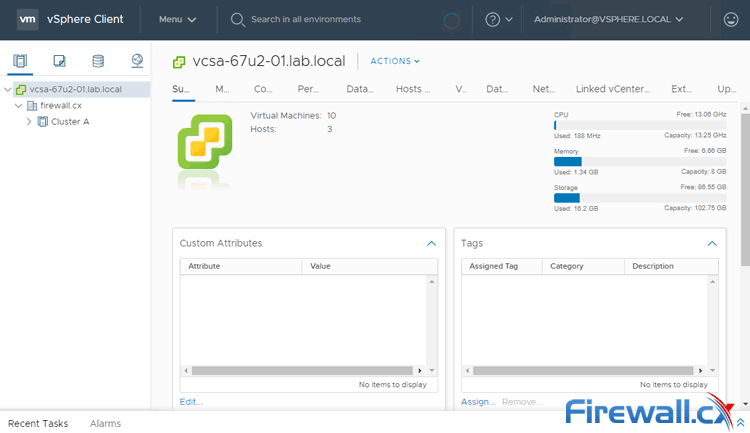
VMware vsphere client - Click to enlarge
VMware Workstation Player vs VMware Workstation Pro
VMware Workstation Player is free software that lets you run a Virtual Machine on top of your own Windows PC’s Operating System. There are two versions of VMware Workstation Player; Workstation Player and Workstation Pro.
The key differences between these two versions are that with VMware Workstation Player you can only run one Virtual Machine on your computer at once and enterprise features are disabled. VMware Workstation Pro on the other hand supports running multiple virtual machines at the same time plus a few more neat features mentioned below.
Here is what Workstation Pro looks like - notice how you can have many virtual machines running at once:
 VMware Workstation Pro - Click to enlarge
VMware Workstation Pro - Click to enlarge
VMware Workstation is essentially an application installed on top of Windows which lets you run connected or isolated Virtual Machines. It’s best suited for developer’s who need access and control to deploy and test code or for systems administrators looking to test applications on the latest version of a particular Operating System, of which over 200 are supported in Workstation Player and Pro.
We’ve already explained that Workstation Player is the free version of Workstation Pro but when it comes to functional differences we’ve detailed those for you below: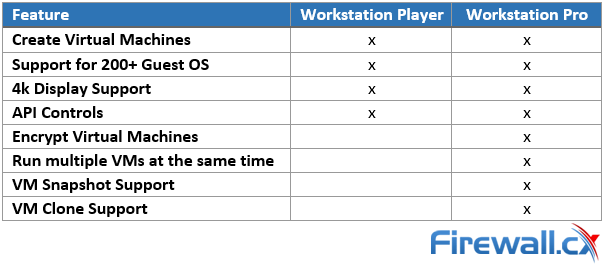 VMware Workstation Player and Pro both get installed onto your Windows PC or Laptop, on which you can run your virtual machines. Pro is interesting because you can run as many Virtual Machines as your Windows PC or Laptop hardware can handle making it a great bit of software for running live product demonstrations or testing without needing access to remote infrastructure managed by another team. The key element here is to ensure your laptop or PC has enough resources available (CPU/Cores, RAM and HDD space) for the Virtual Machines that will be running on it.
VMware Workstation Player and Pro both get installed onto your Windows PC or Laptop, on which you can run your virtual machines. Pro is interesting because you can run as many Virtual Machines as your Windows PC or Laptop hardware can handle making it a great bit of software for running live product demonstrations or testing without needing access to remote infrastructure managed by another team. The key element here is to ensure your laptop or PC has enough resources available (CPU/Cores, RAM and HDD space) for the Virtual Machines that will be running on it.
Diving into some of the features that VMware Workstation Pro provides shows how much value for money that software is; Being able to take a snapshot of Virtual Machines is useful so that you can roll back a Virtual Machine to a particular date and time in just a few seconds. You can also clone Virtual Machines should you need many copies of the same VM for testing. Encryption is also available in the event that your local Virtual Machines contain sensitive information.
VMware Workstation Pro is, therefore, a mini version of ESXi, it’s not capable of clustering features but it is an extremely cost-effective way (Approximately $300 USD) to make use of some of the unused resources on your Windows machine.
Summary
In summary here are our definitions for everything covered in this article:
- vSphere: vSphere is a naming convention or “brand” for a selection of VMware Infrastructure solutions including vCenter Server, ESXi, vSphere Replication and Update Manager.
- vCenter Server: vCenter Server is one of the solutions under the vSphere suite. It is used to manage multiple ESXi servers and enabled cluster level and high availability features for ESXi servers and Virtual Machines. vCenter Server is generally purchased when paid versions of ESXi have been deployed.
- Workstation Player: Workstation Player is free software by VMware that lets you run one Virtual Machine at a time within your Windows Operating System.
- Workstation Pro: Workstation Pro is the same as Workstation Player but it requires a paid license which enables enterprise features such as the ability to run many Virtual Machines from your Windows PC or Laptop. Features such as Virtual Machine snapshots, cloning and encryption are also supported with Pro.
- ESXi: ESXi is the enterprise-grade solution for running Virtual Machines in the datacentre. It is installed onto bare metal servers. There is a basic free version, suitable for labs and test environments but the paid versions are more suitable for running mission-critical virtual machines and applications for your business, enabling cluster level features such as High Availability.
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!















