The Ultimate Guide to Palo Alto Networks Software NGFW (Flex) Credits. How NGFW credits work, Renewal considerations, Online Credit Estimator, Deployment Profiles
 Discover the ins and outs of using Palo Alto Networks’ Software NGFW (Flex) credits to seamlessly renew your cloud-based or virtualized software NGFW devices! Dive into this exciting guide where we unravel the mysteries of software NGFW credits, show you how they're allocated to your deployment profile, and walk you through the renewal and verification process.
Discover the ins and outs of using Palo Alto Networks’ Software NGFW (Flex) credits to seamlessly renew your cloud-based or virtualized software NGFW devices! Dive into this exciting guide where we unravel the mysteries of software NGFW credits, show you how they're allocated to your deployment profile, and walk you through the renewal and verification process.
Learn to calculate your required NGFW credits with the online Credit Estimator and much more. Get ready to master your NGFW credits and keep your network security top-notch!
Key Topics:
- Grasping the Basics of Software NGFW (Flex) Credits
- Estimating Your NGFW Credit Needs with the Credit Estimator
- Renewing Your Deployment Profile with NGFW Credits
- Summary
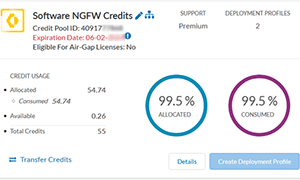
Grasping the Basics of Software NGFW (Flex) Credits
Palo Alto Networks’ Cloud-based (Azure, AWS, GCP) and virtualized (ESXi, Hyper-V, KVM) deployments, aka software NGFW devices, are licensed using Software NGFW credits (Flex Credits). When deploying a software NGFW device, you are required to purchase the correct amount of NGFW credits to allow the deployment, licensing and operation of the device. The amount of NGFW credits required, depend on the specifications of your NGFW device which include:
- Number and type (VM-Series or CN-Series) of firewalls deployed.
- Number of vCPUs per firewall.
- Subscriptions e.g Threat Prevention, URL Filtering, Wildfire etc.
- Management Options e.g Panorama Management, Panorama Log Collector etc.
- Support Options e.g Premium or Platinum support.
NGFW credits are subscription-based, meaning they expire 12 or 36 months after purchase (depending on your contract), regardless of how many credits you use. For example, if you purchase 100 NGFW credits 12-month subscription and use 80 NGFW credits for your deployment, the remaining 20 NGFW credits will be available for consumption, but expire at the end of the contract.
It's crucial to purchase the right amount of NGFW credits to minimize any that go unused.
